Road and Highway Types in India: A Complete Guide to Classifications and Rules

12 Sep 2025
Written by: BikeCarHub Editorial Team
Published on: 19th August 2025
India is home to one of the largest road networks in the world, connecting cities, towns, and even the remotest villages. Roads and highways play a critical role in transportation, trade, tourism, and daily commuting. But not all roads are the same. They are built and classified based on their purpose, connectivity, and importance in the country’s infrastructure.
BikeCarHub provides a detailed guide to the types of roads and highways in India, their classification by the Indian Road Congress (IRC), driving rules, signage, speed limits, penalties, and essential tips for safe travel. Whether someone is a new driver, a regular commuter, or a road trip enthusiast, understanding these aspects ensures safer and more enjoyable journeys.
Classification of Roads and Highways as per Indian Road Congress (IRC)
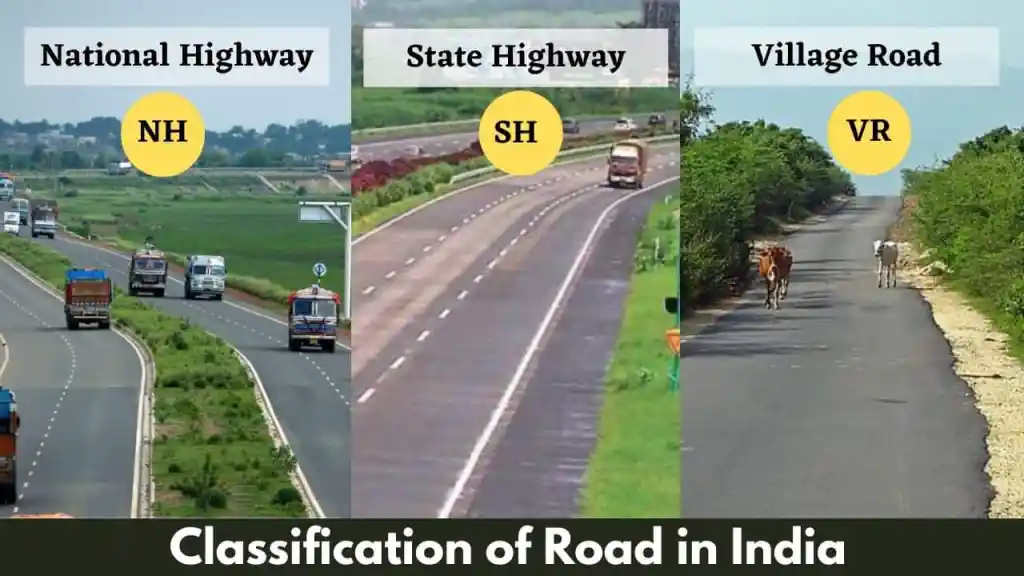
The Indian Roads Congress (IRC) is the authority responsible for road standards and classification in India. According to the IRC, roads are divided into different categories to streamline planning, construction, and maintenance. The four major classifications are:
1. National Highways (NHs)
National Highways form the backbone of India’s road transport system.
- Purpose: .They connect major cities, ports, capitals, and industrial hubs.
- Administration: .Maintained by the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI).
- Features: . Wider lanes, multiple carriageways, toll plazas, and modern infrastructure.
- Examples: . Delhi–Mumbai Expressway, NH 44 (India’s longest highway from Srinagar to Kanyakumari).
These roads are essential for interstate travel, goods movement, and defense purposes.
2. State Highways (SHs)
State Highways connect major cities within a state and link them to National Highways.
- Purpose: .Facilitate trade and travel inside the state.
- Administration: .Managed by state Public Works Departments (PWDs).
- Features: . Generally narrower than NHs but well-maintained for inter-district travel.
- Example: .Mumbai–Pune Highway in Maharashtra.
They play a key role in regional development by linking towns, markets, and industrial zones.
3. District Roads
District roads provide connectivity between towns, villages, and district headquarters.
- Types:
- Major District Roads (MDRs): Connect towns with markets, industries, and SHs.
- Minor District Roads: Provide local access to villages and nearby settlements.
- Administration: Maintained by District Authorities or Zilla Parishads.
These roads act as feeders to highways and support local economies.
4. Rural Roads
Rural roads, also known as village roads, connect small villages to nearby towns and cities.
- Purpose: Provide access for rural populations to schools, hospitals, and markets.
- Schemes: Programs like Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) have improved rural connectivity.
- Features: Usually single-lane, may be unpaved in remote regions.
These are the lifelines of India’s villages, enabling social and economic growth.
Types of Highways in India: Understanding Your Road
Highways in India are further classified based on design and usage:
1.Expressways:
- Access-controlled, six to eight lanes.
- High-speed roads for long-distance travel.
- Example: Yamuna Expressway.
2.National Highways:
- Four to six lanes, covering long distances.
3.State Highways:
1.- Two to four lanes, connecting state regions.
4.District and Rural Roads:
- Single or double lanes.
Types of Lanes on Highways
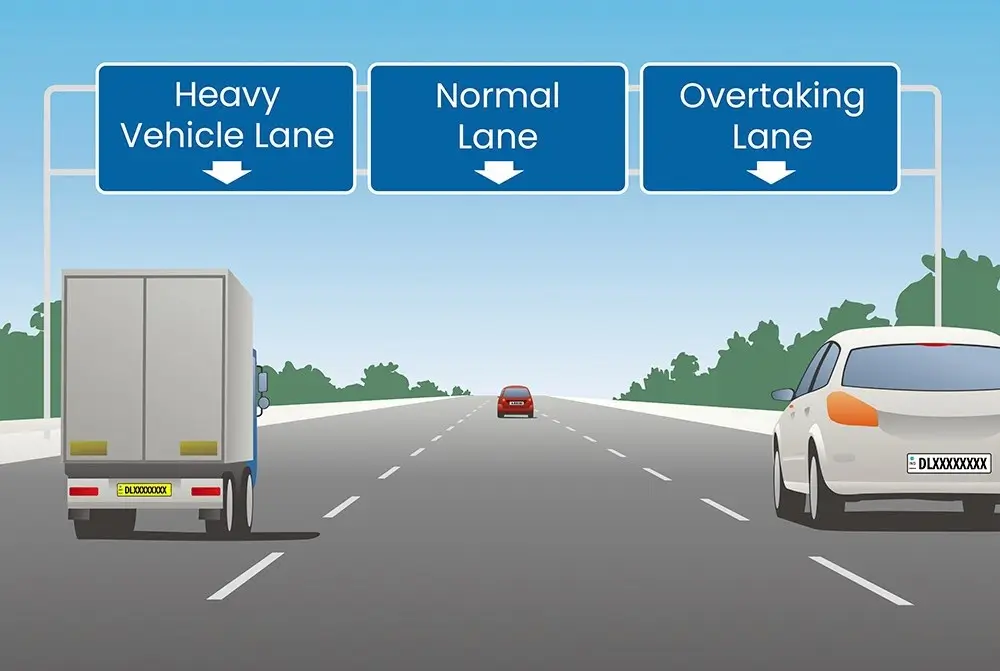
Highways in India often have multiple lanes. Each lane serves a purpose:
- Left Lane (Slow Lane): For heavy vehicles and slower traffic.
- Middle Lane: For regular traffic flow.
- Right Lane (Fast Lane): For overtaking and faster-moving vehicles.
Understanding lane usage ensures smooth traffic flow and reduces accidents.
Highway Driving Rules in India
Driving on highways requires discipline and awareness. Key rules include:
- Always drive on the left side of the road.
- Use the right lane only for overtaking.
- Follow traffic signs and signals.
- Maintain a safe distance from the vehicle ahead.
- Avoid rash driving and unnecessary lane changes.
Speed Limits on Indian Highways: What’s Legal and Safe?

The government defines speed limits for different vehicles:
- Cars: 100–120 km/h on expressways, 80–100 km/h on highways.
- Two-wheelers: 80 km/h on highways.
- Heavy Vehicles: 60–80 km/h.
Safe driving means following posted speed limits and adjusting speed during rain, fog, or heavy traffic.
Speed Limits on Indian Roads (As per MoRTH Guidelines)
| Vehicle Type | Expressways | National & State Highways | City / Urban Roads |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cars / Light Vehicles | Up to 120 km/h | 100 km/h (generally) | 50–70 km/h |
| Two-Wheelers | Up to 80 km/h | 80 km/h | 40–50 km/h |
| Buses & Light Commercial Vehicles | 100 km/h | 90 km/h | 40–50 km/h |
| Heavy Trucks & Multi-axle Vehicles | 80 km/h | 60–80 km/h | 30–40 km/h |
Lane Discipline & Overtaking Rules
- Always overtake from the right side.
- Do not overtake on curves, slopes, or crowded intersections.
- Use indicators and horns cautiously when overtaking.
- Never cut off another vehicle abruptly after overtaking.
Lane discipline reduces accidents and ensures smoother traffic.
Important Signage & Symbols You Should Know

Traffic signs are categorized as:
- Mandatory Signs: Stop, Speed Limit, No Entry.
- Cautionary Signs: Sharp Turn, School Ahead, Animal Crossing.
- Informatory Signs: Petrol Pump, Hospital, Rest Area.
These symbols guide drivers and ensure road safety.
Understanding Road Markings
Road markings provide crucial information:
- Solid White Line: No lane change or overtaking.
- Broken White Line: Lane change permitted with caution.
- Double Yellow Line: Overtaking prohibited in both directions.
Drivers must pay attention to these markings as they indicate safe driving practices.
Common Road Markings in India and Their Meanings
| Road Marking | Appearance | Meaning / Rule for Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| Solid White Line | Continuous white line on the road | No lane changing or overtaking allowed. Stay within your lane. |
| Broken White Line | Dashed white line in the center | Lane changing and overtaking permitted, but with caution. |
| Double White Line | Two parallel solid white lines | Strict lane discipline, no crossing or overtaking. |
| Single Yellow Line | Continuous yellow line | No overtaking in both directions; separates opposing traffic flows. |
| Double Yellow Line | Two parallel continuous yellow lines | Overtaking strictly prohibited; indicates high-risk road section. |
| Zebra Crossing | Alternating white stripes | Pedestrian crossing zone; vehicles must stop for pedestrians. |
| Stop Line | Thick solid white line before signals | Vehicles must stop before this line when traffic signal is red. |
Handling Emergencies on the Highway
Emergencies can happen unexpectedly. Some important steps are:
- Park the vehicle on theshoulder or emergency lane.
- Switch on hazard lights.
- Place a reflective triangle behind the vehicle.
- Call emergency helplines for assistance.
Being prepared ensures safety during breakdowns or accidents.
Emergency Contact Numbers
- Police: 112 (all-in-one helpline)
- Ambulance: 108
- Fire: 101
Drivers should save these numbers for quick access during emergencies.
Penalties for Violating Highway Driving Rules
India has strict penalties under the Motor Vehicles Act:
- Over-speeding: ₹1,000–₹2,000.
- Drunken Driving: ₹10,000 and/or imprisonment.
- Not wearing a seat belt or helmet: ₹1,000.
- Dangerous Driving: ₹5,000 and license suspension.
These fines encourage responsible driving habits.
Penalties for Violating Highway Driving Rules in India
| Offense / Violation | Penalty / Fine (₹) | Additional Action |
|---|---|---|
| Over-speeding | ₹1,000 – ₹2,000 (light vehicles) ₹2,000 – ₹4,000 (heavy vehicles) |
Possible license seizure for repeat offense |
| Drunken Driving | ₹10,000 and/or 6 months imprisonment (first offense) | Higher penalties for repeat violations |
| Dangerous / Rash Driving | ₹5,000 | License suspension possible |
| Driving Without License | ₹5,000 | Vehicle impound in some cases |
| Not Wearing Seat Belt | ₹1,000 | — |
| Riding Without Helmet/td> | ₹1,000 and license disqualification for 3 months | — |
| Using Mobile While Driving | ₹5,000 | — |
| Overloading Vehicle | ₹2,000 per ton + ₹1,000 (general fine) | — |
| Driving Without Insurance | ₹2,000 (first offense) ₹4,000 (subsequent offense) |
— |
| Hit and Run (not reporting) | ₹10,000 fine and/or imprisonment | — |
Golden Tips for Highway Driving in India

- Always wear a seatbelt or helmet.
- Avoid night driving unless necessary.
- Keep the vehicle well-maintained.
- Carry essential documents (DL, RC, Insurance, PUC).
- Take breaks every 2–3 hours during long trips.
- Never use a mobile phone while driving.
- Stay alert for pedestrians, stray animals, or slow vehicles.
Summary
India’s road network is vast and diverse, ranging from expressways and national highways to state highways, district, and rural roads. Understanding the classification, rules, speed limits, signage, and penalties helps drivers stay safe and compliant. Highways demand discipline, awareness, and responsibility. By following traffic rules and respecting fellow road users, journeys can be safe, efficient, and enjoyable.
FAQs About Roads and Highways in India
Royal Enfield Motors Click Here!
For Suzuki Motors Click Here!
Check other Vehicles on BikeCarHub





BikeCarHub | 5 Dec 2024


BikeCarHub | 29 Nov 2024



Popular Brands
Compare Bikes

Honda Activa 125 vs TVS Jupiter

Royal Enfield Bullet350 vs TVS Apache RR310

Bajaj Pulsar 150 vs Bajaj Pulsar 125

Yamaha R3 vs Bajaj Pulsar NS200

Bajaj Pulsar RS200 vs Bajaj Pulsar NS200

TVS Apache RTR 160 4V vs Bajaj Dominar 250

TVS Ronin vs Royal Enfield Hunter 350

Suzuki Access 125 vs Honda Activa 125

Suzuki Gixxer vs TVS Apache RTR 160

TVS Radeon vs Hero Splendor Plus































































